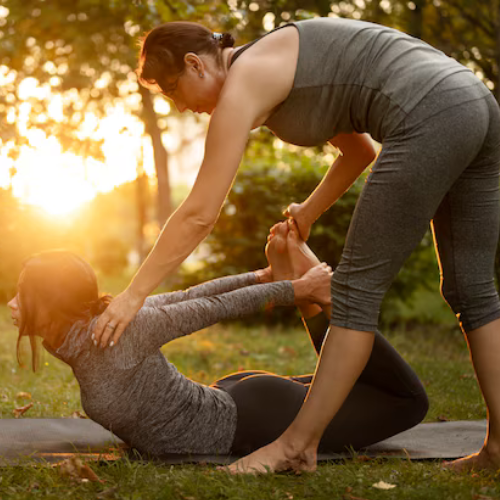
Therapeutic Exercise
Therapeutic exercise, also known as physiotherapy or rehabilitative exercise, encompasses a wide range of physical activities and movements designed to restore, maintain, or enhance physical function, flexibility, strength, endurance, and overall well-being. It's a cornerstone of physical therapy and rehabilitation programs aimed at treating various musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiopulmonary, and other health conditions.
At its core, therapeutic exercise is tailored to each individual's specific needs, taking into account their medical history, current physical condition, functional limitations, and treatment goals. Whether someone is recovering from surgery, managing chronic pain, rehabilitating from an injury, or coping with a neurological disorder, therapeutic exercise can play a crucial role in their recovery journey.
The goals of therapeutic exercise are multifaceted. It aims to improve range of motion, flexibility, and joint mobility, which can alleviate stiffness, reduce pain, and enhance overall physical function. Strengthening exercises target weakened muscles,
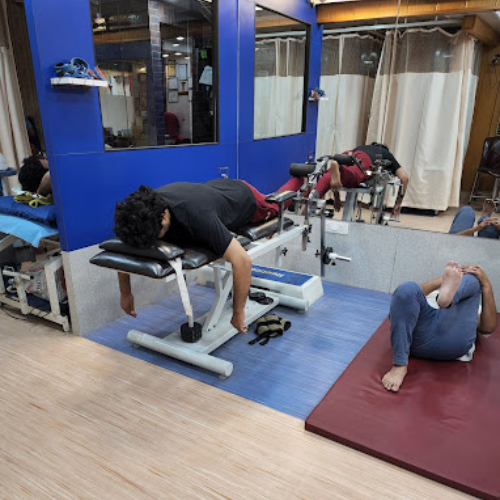

helping to restore muscle balance and stability around joints, which is essential for injury prevention and optimal movement patterns. Endurance exercises focus on increasing cardiovascular fitness and stamina, promoting energy conservation and enhancing the ability to perform daily activities with less fatigue.
Range of motion exercises: These involve moving joints through their full range to maintain or improve flexibility and prevent stiffness.Strength training: This includes exercises using resistance, such as weights, resistance bands, or body weight, to strengthen muscles weakened by injury, surgery, or disuse.
Balance and coordination exercises: These aim to improve proprioception and neuromuscular control, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing functional mobility.
Cardiovascular exercises: Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming are utilized to improve heart and lung function, enhance circulation, and boost overall endurance.
Functional exercises: These mimic activities of daily living, such as squatting, lifting, reaching, or walking, to improve the ability to perform these tasks safely and efficiently.
In addition to physical benefits, therapeutic exercise can have positive effects on mental health and well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity releases endorphins, neurotransmitters that promote feelings of happiness and reduce stress and anxiety. Moreover, the sense of accomplishment and progress achieved through therapeutic exercise can boost self-confidence and motivation, contributing to a more positive outlook on recovery and rehabilitation.
Overall, therapeutic exercise is a fundamental component of holistic healthcare, promoting physical, psychological, and emotional well-being by empowering individuals to actively participate in their own healing process and achieve optimal functional outcomes. Through personalized and targeted interventions, therapeutic exercise enables individuals to regain independence, improve quality of life, and reclaim control over their health and mobility.